Trusted Employment
and Labour Lawyer
Receive proactive legal solutions that will protect your interests whatever the nature of your employment issue is

Patrola Law has been chosen as a top business law firm for four consecutive years (2019-2022) by Three Best Rated and trusted by clients with a 4.8 star rating on Google.
From wrongful dismissal to payment disputes, workplace discrimination, harassment complaints, and other nature of employment issues;
our experienced employment and labour legal counsel will provide you with clear advice and take care of you every step of the way
Safeguard your employment rights by scheduling a consultation today
I am an Employee
Patrola Law provides practical employment law solutions for employees in the following areas:
I am an Employer
Patrola Law provides practical employment law solutions for employers in the following areas:
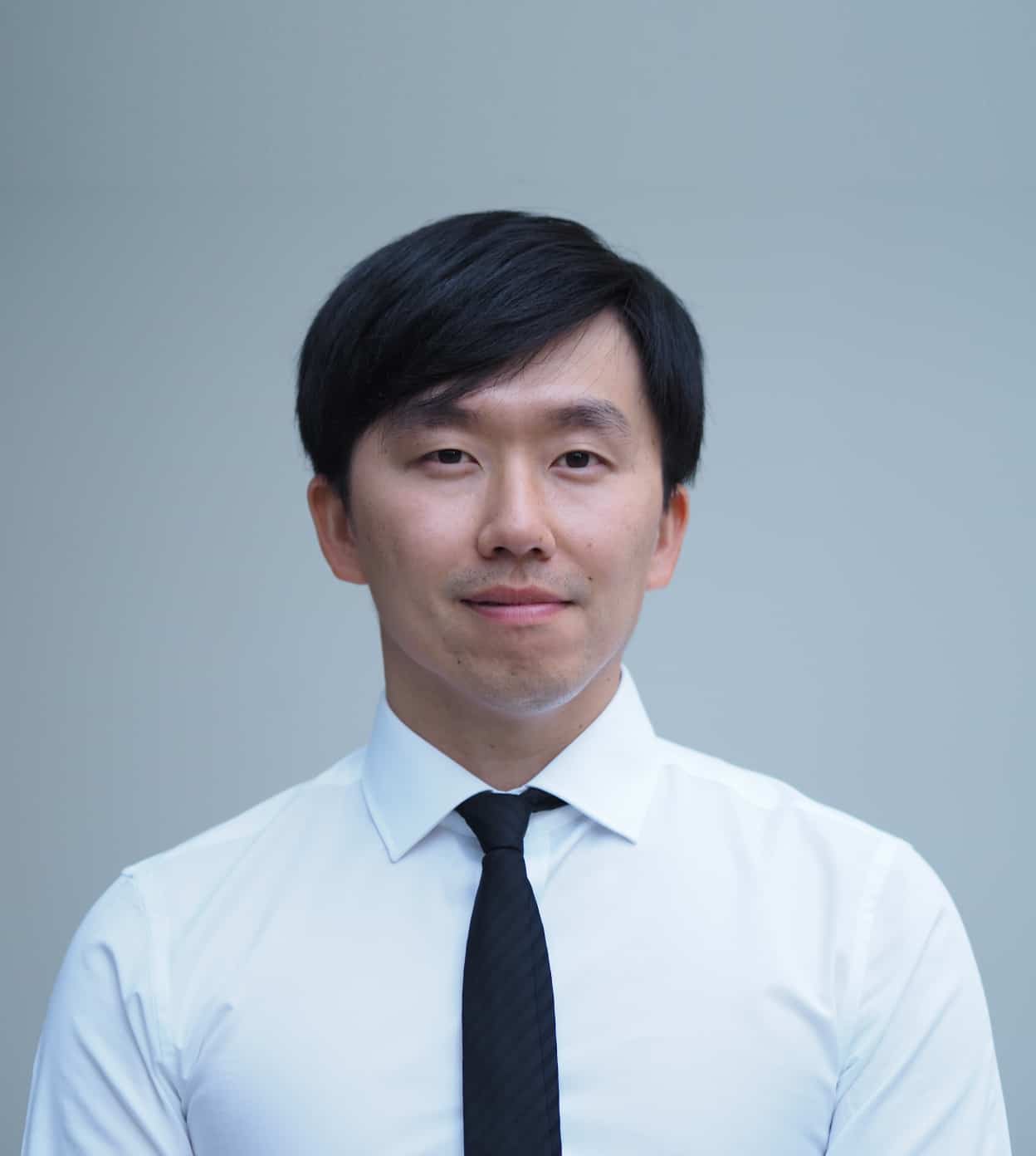
Allow me to guide you through the legal complexities and fight for your workplace rights
With a pro-active and no-nonsense approach, I am committed to helping you understand your rights and resolving your employment issues effectively.
I genuinely understand the importance of practical and cost-effective solutions, and I strongly advocate for my clients with this goal in mind. Your well-being and rights matter to me, and I'll work tirelessly to achieve a favorable outcome for you.
Let's tackle these challenges together and pave the way for a better workplace environment.
Take the first step towards a positive workplace outcome
Frequently Asked Questions
If you have an employment contract, severance pay may refer to previously agreed upon compensation that you can receive at the end of your employment. If you do not have an employment contract, severance pay refers to earnings you are entitled to receive in lieu of advance notice.
No. But whether or not there was cause is usually heavily disputed.
Yes, if there is no dispute between you and the employer that there was no fault on your part, then you are entitled to severance pay (or at least working notice).
You and the employer may end up negotiating a severance package for weeks if not months. However, you are entitled to a minimum amount under the Employment Standards Act, and the employer should provide you with that pay right away.
Under the Employment Standards Act, you must be employed for a consecutive period of three months to be entitled to severance pay. If you are a fixed term employee and/or was actively induced to join the company, you should consider pursuing your claims under common law.
It may depend on contextual factors, but wages cannot be deducted for simply making a mistake on the job.
As long as you are being paid minimum wages and are paid in accordance with your employment contract, it would be difficult to hold an employer to his word that "he would give you a raise in the future". If there was a concrete agreement in place (how much raise and when it will be effective, etc.), you should consider speaking to an employment lawyer.
Your statutory termination pay maxes out at 8 weeks.
Yes, there is at least one ruling from the Employment Standards Tribunal that has applied the legislation to an Alberta-based employee. However, other circumstantial factors may swing the decision the other way, so you should consult an employment lawyer.
If you sign the new agreement, you would likely keep your job (for some time, at least) but you may be waiving some very significant rights that you were entitled to under your old contract. You should speak to an employment lawyer right away.
Any employer has the right to terminate an employee at any time, as long as the employee is given advance notice or pay in lieu. If the employer can make a business case that he needs an employee who will work on the holidays, your refusal to work could very well mean termination.
You are entitled to two weeks vacation only after completing one (1) full year of employment. After five (5) years of employment with the same employer, you would be entitled to three weeks vacation per year.
You must be given at least half an hour meal break during your shift. An employer must not make you work for more than 5 consecutive hours without a meal break. That means on a day you are working overtime, you may be entitled to two meal breaks.
NO. But if you are carrying out your job duties on your lunch break, then you are still working on your lunch break and you should be paid for that.
If the teenager is under the age of 15, you will need to get the consent of the child's parent or legal guardian. You may not employ a child under the age of 12, unless you have the consent of the Director of Employment Standards. There are some exceptions for hiring children in the entertainment/film industry.
Related Posts
Ensure your rights are upheld.
Simply fill out the form below to schedule a call.